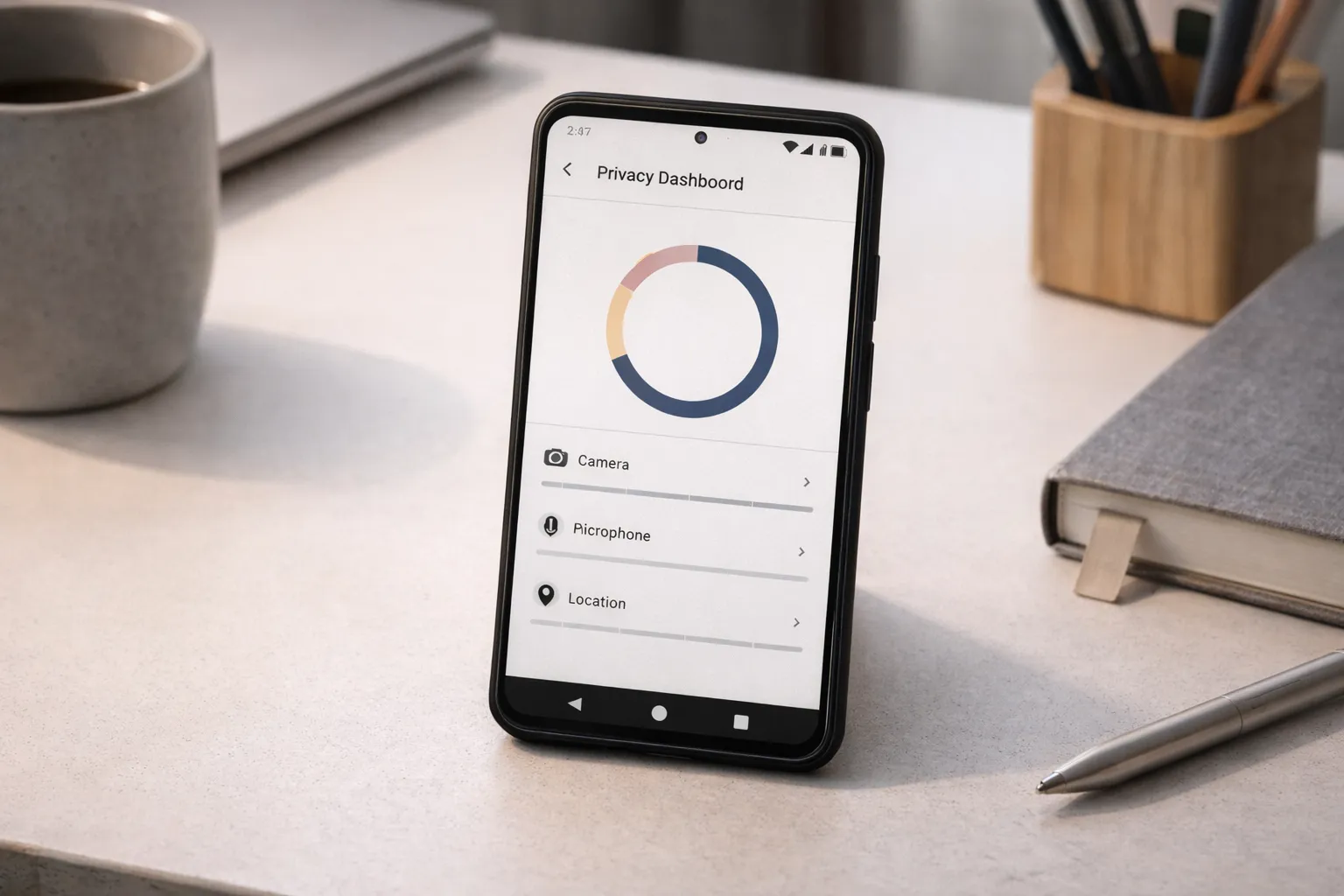
What Is RAM Expansion & Should You Turn It Off? (2025 Guide)
RAM Expansion—also called Virtual RAM, Extended RAM, or Memory Expansion—lets an Android phone treat a portion of its internal flash storage as extra working memory. In 2025, most OEMs ship this feature in settings under names like "Memory Extension", "Virtual RAM", or "Extended RAM". This guide explains how it works, where it helps (and where it doesn't), provides a simple test protocol you can run in 10–20 minutes, and shows how to decide whether to keep it enabled on your device.
Before you change settings, bookmark the related optimization guides for reference: Android Speed HUB, Clear Cache, and Fix App Crashes.
Table of Contents
- What Is RAM Expansion?
- How Does RAM Expansion Work (Tech Essentials)
- Common OEM Implementations
- Practical Benefits
- Potential Downsides & Trade-offs
- Real-world Test: Method & Example Data
- How to Measure Impact (KPIs & CSV)
- Who Should Keep It On vs Turn It Off
- Vendor-Specific Notes (Samsung, Xiaomi, Realme, Google)
- How to Enable/Disable RAM Expansion (Step-by-step)
- Troubleshooting & Best Practices
- 30‑Day Performance Check Plan
- Related Guides (Android Speed HUB)
- Final Verdict
What Is RAM Expansion?
RAM Expansion borrows a slice of your phone’s internal storage and exposes it to the OS as additional working memory (swap). It is essentially a managed swap file or partition that the memory manager uses when physical RAM is exhausted. On devices with limited RAM (4–6GB), this can reduce app reloads and improve multitasking. However, it is not a substitute for physical RAM in latency-sensitive tasks.
How Does RAM Expansion Work (Tech Essentials)
At a high level, there are two ways Android systems extend memory:
- Swap (virtual RAM): Uses a portion of storage as a swap area. The kernel moves inactive pages from RAM into the swap to free up RAM for active tasks.
- zRAM / compressed RAM: Compresses RAM pages to fit more data into physical RAM without using storage; some OEMs use a hybrid of compression + swap.
Important performance note: NAND flash (UFS) is orders of magnitude slower in random access and has higher latency than DRAM. Typical DRAM throughput is tens of gigabytes per second while UFS writes can be in the low gigabytes per second (sequential) and much lower for random writes. That means moving active working sets to storage will be slower, but for background pages (cold tabs, paused apps) it can still be a net win for responsiveness.
What actually changes when you enable it
- OS reports a higher "available" memory pool to the scheduler.
- Background apps are less likely to be killed, so switching back resumes them without reload.
- Storage write activity increases slightly whenever pages are swapped to disk.
Common OEM Implementations
- Samsung: "RAM Plus" — offers 2–8GB of expansion depending on model; tuned to reduce background app kills while aggressively limiting writes.
- Xiaomi/Redmi: "Memory Extension" — configurable sizes and a visible toggle in Settings on most ROMs.
- Realme/OPPO/Vivo: "Extended RAM" — often bundled with other performance modes.
- Google Pixel: Pixel devices historically favored aggressive memory management; some Pixel builds now include zRAM-centric approaches rather than large swap files.
Implementation details matter: some OEMs use compressed RAM first and only swap to flash as a last resort, which reduces write amplification and preserves battery life.
Practical Benefits
- Fewer app reloads: Switch between 8–12 apps and you’ll likely see fewer cold restarts on a 4–6GB device with RAM expansion enabled.
- Smoother multitasking: Background services and widgets remain resident longer, improving the feel of task switching.
- Lower visible "stutter" in everyday use: For social media, messaging, and email, perceived snappiness often improves.
- Cost-effective upgrade: For older devices, enabling memory expansion provides many of the multitasking benefits of higher-RAM models without hardware changes.
Potential Downsides & Trade-offs
- Latency penalties: Swapping a page in from UFS is slower than DRAM, which can cause short hitches when a swapped-in page is needed immediately.
- Battery & thermal impact: Extra I/O activity and CPU interrupts for swap management can have a small but measurable impact on battery and surface temperature during heavy background churn.
- Storage wear: Flash has finite write endurance. Modern UFS chips are robust (many TBs written), but heavy swap use over years may slightly increase wear. For most users this is a theoretical concern rather than an immediate problem.
- No FPS gains: RAM expansion does not improve GPU memory bandwidth or frame rendering; games will not run faster because of it.
Real-world Test: Method & Example Data
To judge whether RAM expansion helps your device, run a short, repeatable test. You need 20–30 minutes total and a stopwatch.
Test setup (10–15 minutes)
- Charge to >40% and disable battery saver.
- Close all apps, reboot the device, and wait 30s for background services to settle.
- Open and sign into apps you normally use (Chrome with 10 tabs, Instagram, Twitter/X, YouTube, Slack, a game).
- Record baseline: open each app in turn, then switch through them rapidly for 10 minutes and count reloads (times the app had to fully reload content or restart).
- Repeat the entire sequence with RAM expansion toggled (on ↔ off) and compare reload counts and time-to-resume.
Example — 6GB phone (illustrative)
- Baseline (RAM expansion off): App reloads during the run = 9; average resume time = 900ms.
- With RAM expansion on: App reloads = 3; average resume time = 1,100ms.
- Interpretation: reloads dropped by ~66% at the cost of a marginally higher resume latency when a swapped page is needed — a clear win for multitaskers who prefer fewer reloads.
Note: your mileage will vary by device, ROM, and storage type (UFS 3.x vs UFS 2.x vs eMMC).
How to Measure Impact (KPIs & CSV)
Track a few simple KPIs during testing. Use a CSV with these headers to record runs:
date,device_model,physical_ram_gb,ram_expansion_setting,run_time_min,app_reload_count,avg_resume_ms,peak_resume_ms,observed_battery_drop_pct
Collect 2–3 runs per setting and compare averages. Focus on the app reload count and average resume time — those are the clearest indicators of perceived multitasking improvement.
Who Should Keep It On vs Turn It Off
- Keep it ON: Devices with 3–6GB RAM, heavy multitaskers who prefer fewer reloads, users who reference many apps for short periods throughout the day.
- Turn it OFF: Flagship devices with 8–16GB RAM, competitive mobile gamers, and users who prioritize lowest possible latency and maximum battery life.
Vendor-Specific Notes (Samsung, Xiaomi, Realme, Google)
- Samsung (RAM Plus): Conservative by default; the system favors compressed RAM first and writes to flash more sparingly.
- Xiaomi / Redmi: Memory Extension is user-configurable on many models — test both off and on and keep the setting that gives more consistent performance for your usage.
- Realme / OPPO / Vivo: Typically offer a toggle and sometimes dynamic management tied to performance modes — be cautious with aggressive "performance" profiles that increase writes.
- Google Pixel: Focuses on aggressive memory management and zRAM; Pixel users may see less benefit from large swap-based expansion features.
How to Enable / Disable RAM Expansion (Step-by-step)
Settings menu names vary by OEM; here's a short reference (see your Settings search if you can’t find it):
- Samsung: Settings → Battery and device care → Memory → RAM Plus → Toggle
- Xiaomi / Redmi / POCO: Settings → About phone → Memory Extension → Toggle
- Realme / OPPO: Settings → Additional Settings → RAM Expansion → Toggle
- Vivo / iQOO: Settings → RAM & Storage → Extended RAM → Toggle
- Pixel / AOSP-ish: May be under Developer options or absent; check OEM docs.
Troubleshooting & Best Practices
- If the phone feels sluggish after enabling: try a smaller expansion size (many phones offer 1–2GB steps) or leave it disabled.
- If battery drains noticeably: test with and without the feature for 24 hours and compare battery % drop and temperature logs — refer to our overheating guide for diagnosing thermal issues.
- Keep storage free: Low free storage reduces the effectiveness of virtual RAM — clear cache and unnecessary files per our cache cleanup guide.
- Watch for excessive writes: if you see very high storage write rates over short periods, revert the setting and consult vendor forums or support.
30‑Day Performance Check Plan
- Week 1: Baseline runs — record 3 runs with RAM expansion OFF and ON (CSV). Note app reloads and resume times.
- Week 2: Daily spot checks — open your top 8 apps and note if background reloads occur.
- Week 3: Battery & thermal observation — compare battery drain and device surface temperature for similar usage windows.
- Week 4: Re-evaluate — keep the configuration that gives the best balance of fewer reloads and acceptable battery/thermals.
Related Guides (Android Speed HUB)
- How to Speed Up Your Android Phone in 2025
- Clear Cache to Boost Speed & Free Storage
- How to Fix App Crashes on Android
- Why Is My Phone Overheating? Causes & Fixes
- Force 90Hz/120Hz Refresh Rate
Final Verdict
RAM Expansion is a pragmatic, low-risk feature for devices with limited physical memory. For most users on 4–6GB phones, it reduces app reloads and improves the feel of multitasking. For power users and gamers on high-RAM devices, disabling it delivers slightly lower latency and better battery life. Use the short test in this guide.