Is Your Phone Listening to You? How to Stop Google & Apps from Tracking (2026 Privacy Guide)
Have you ever talked about something and suddenly seen ads related to it? Many people believe their phone is secretly listening. But is that true?
In this complete 2026 privacy guide, we’ll explain what’s really happening, why it feels like your phone is listening, how tracking actually works, and the exact steps to stop Google and apps from tracking you on Android.
If you're serious about protecting your device, you should also read our Google Account Security Checklist (2026) for complete account-level protection.
Table of Contents
- Is Your Phone Really Listening?
- The Microphone Myth Explained
- Why It Feels Like Your Phone Is Listening
- How AI Behavior Tracking Works in 2026
- How Google & Apps Actually Track You
- Ad Personalization & Data Profiling
- Why This Is a Serious Privacy Risk
- Disable Microphone Access on Android
- Turn Off Google Ad Personalization
- Disable Web & App Activity Tracking
- Use Android Privacy Dashboard to Monitor Apps
- Step-by-Step: How to Stop Tracking on Android (2026)
- Final Verdict: Is Your Phone Spying?
Is Your Phone Really Listening?
Short answer: No, your phone is not constantly recording your private conversations to show ads.
This belief has become common because ads sometimes appear related to recent conversations. However, companies like Google use advanced data analysis — not secret audio spying — to predict your interests.
Here’s what actually powers those “creepy accurate” ads:
- Search history – What you look up on Google or YouTube
- Browsing behavior – Websites you visit and products you view
- App activity – How you interact with installed apps
- Location data – Places you visit regularly
- Ad engagement – Ads you click, skip, or watch
This data allows AI systems to build a behavioral profile. For example, if you search for fitness tips, watch workout videos, and visit a sports store, you may start seeing protein supplement ads — even if you never spoke about it.
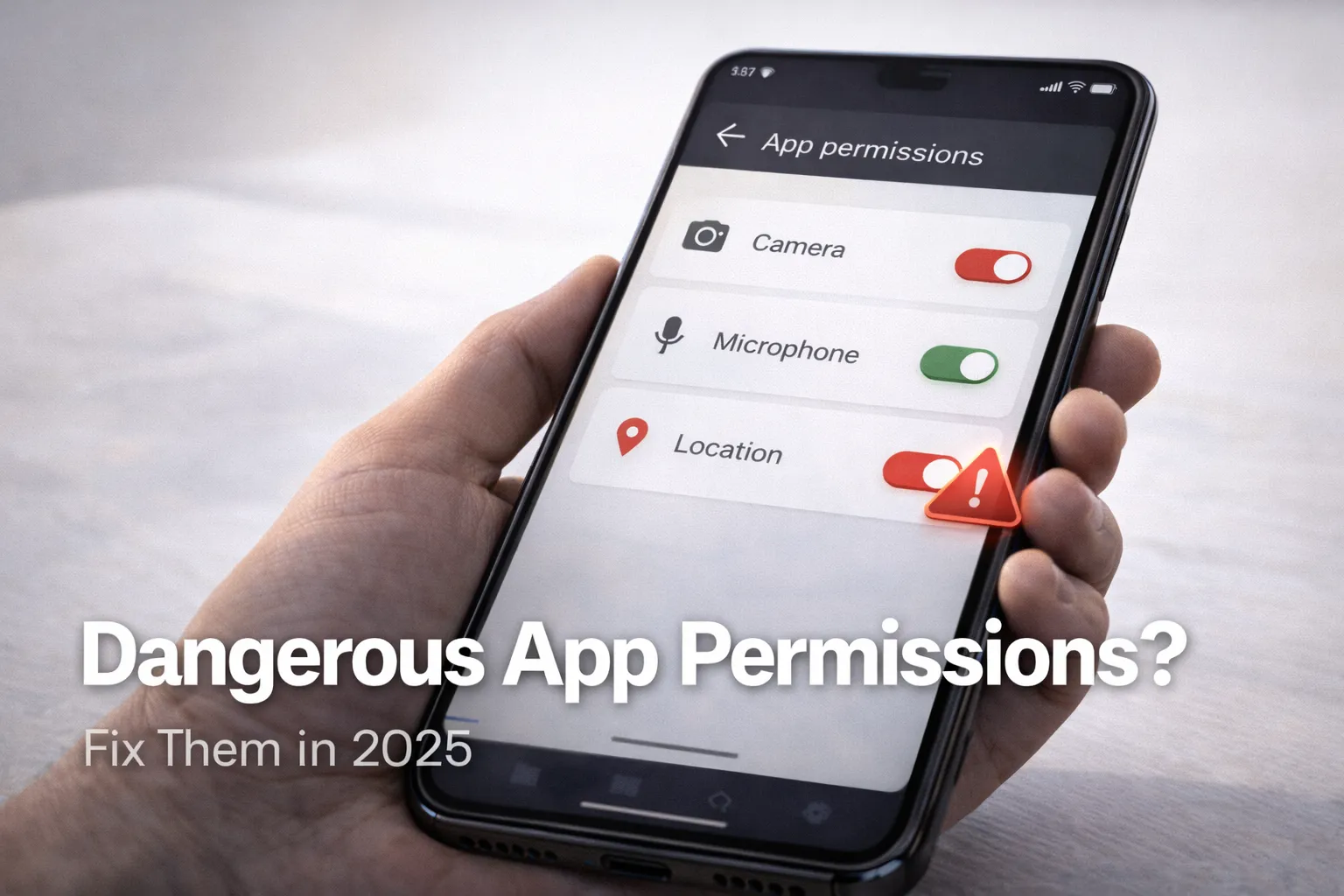
In most cases, the microphone is only activated when you give permission (for example, voice search). You can verify which apps have access by reviewing your App Permissions settings or by checking the Android Privacy Dashboard.
Conclusion: Your phone isn’t secretly listening 24/7. Instead, powerful data tracking and predictive algorithms create the illusion of eavesdropping. Understanding this difference is the first step toward improving your digital privacy.
The Microphone Myth Explained
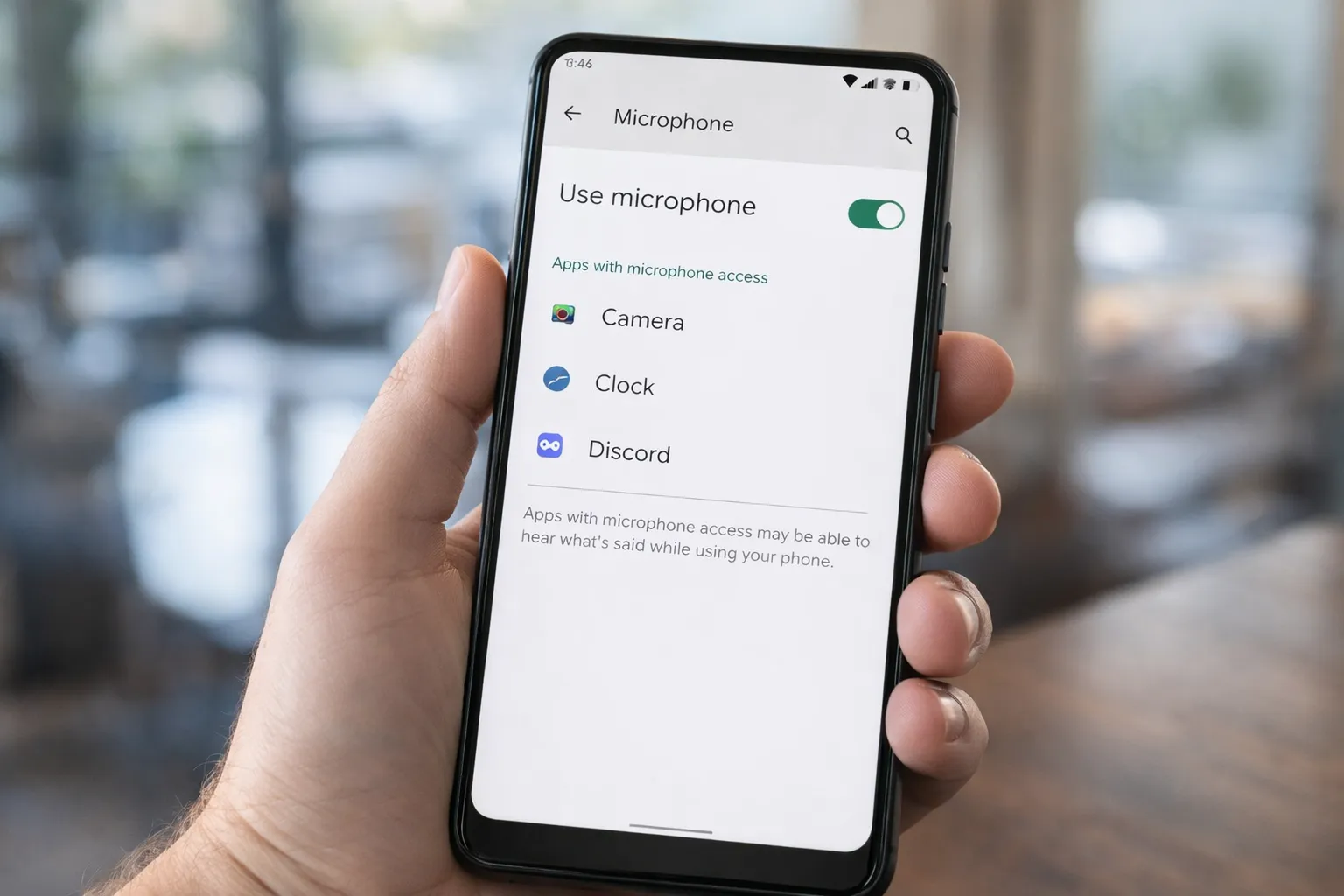
One of the biggest privacy fears in 2026 is the idea that your phone’s microphone is secretly recording everything you say for advertising purposes. In reality, this is highly unlikely.
Here’s why the “always listening” theory doesn’t hold up:
- Battery Drain: Constant audio recording would significantly reduce battery life.
- Massive Data Usage: Sending continuous audio to servers would consume huge amounts of mobile data.
- Legal Risks: Companies like Google would face severe legal consequences if caught secretly recording users.
- Permission Controls: Android requires apps to request microphone access before using it.
Most apps only activate the microphone when you use features like voice search, voice notes, or calling. You can manually verify this by checking which apps have microphone permission in your settings. If you’re unsure how to do that, follow this step-by-step guide on checking and fixing dangerous app permissions on Android.
Additionally, Android shows visual indicators (a green dot) whenever the microphone is in use. You can monitor recent access history using the Android Privacy Dashboard.
Bottom line: The microphone myth feels real because ads are highly targeted — but targeting is powered by behavioral data, not secret recordings. Reviewing your permissions regularly is the smartest way to stay in control of your privacy.
Why It Feels Like Your Phone Is Listening
If your phone isn’t secretly recording you, then why do ads sometimes appear right after a conversation? The answer lies in advanced data prediction and human psychology.
Here’s why it feels creepy:
- Advanced Algorithms: Modern AI systems analyze your behavior across apps, searches, and browsing history to predict what you might be interested in next.
- Previous Searches: You may have searched, viewed, or clicked something related days or weeks earlier.
- Connected Data Signals: People around you (same Wi-Fi, location, or shared interests) may have searched similar topics.
- Behavioral Profiling: Platforms build interest categories based on your activity, not your conversations.
For example, if you recently visited a shopping website, watched related videos, and followed similar pages, targeted ads are expected. It’s pattern recognition — not eavesdropping.
This phenomenon is strengthened by confirmation bias. You notice ads that match your conversations but ignore thousands that don’t. That selective attention creates the illusion of constant listening.
If you want to reduce this tracking effect, review your Google Account activity settings and regularly check app-level permissions using this guide on dangerous app permissions.
Key takeaway: It feels like your phone is listening because AI is extremely good at predicting behavior — not because it is secretly recording your conversations.
How AI Behavior Tracking Works in 2026
![]()
In 2026, AI-powered tracking is more advanced than ever. But it doesn’t rely on secretly recording conversations. Instead, it uses behavioral signals collected from your digital activity.
Here’s how AI behavior tracking typically works:
- Search & Watch History: What you search on Google or watch on YouTube helps platforms understand your interests.
- App Usage Patterns: How long you use certain apps and what features you interact with.
- Location Data: Frequent visits to gyms, malls, or restaurants create lifestyle categories.
- Ad Interactions: Ads you click, ignore, or engage with refine your profile further.
- Cross-Device Signals: Activity across phone, tablet, and desktop may be linked to the same account.
AI systems combine these data points to create an interest-based profile. This allows highly targeted ads and recommendations without needing microphone recordings.
To see what data is being tracked, review your Google Account activity controls and disable unnecessary tracking options. You can also monitor recent camera, microphone, and location access using the Android Privacy Dashboard.
Important: AI tracking is mostly automated and based on patterns — not personal spying. Understanding how it works helps you take smarter steps to limit data collection and improve your privacy.
How Google & Apps Actually Track You
Most tracking on Android happens through permissions and account-based activity — not secret spying. Understanding these methods helps you control your privacy better.
1. Microphone Permission
Apps can access your microphone only if you grant permission. This is typically required for voice search, calls, or voice messages. Android also shows a visual indicator whenever the microphone is active.
2. Location Tracking
Location data is one of the strongest behavioral signals. Even background location access can reveal:
- Places you frequently visit
- Your daily routine
- Shopping or lifestyle habits
Limiting location access to “Allow only while using the app” reduces unnecessary tracking.
3. Ad Personalization
Your Google account tracks activity across apps, Chrome browsing, YouTube, and other services. This data is used to personalize ads and recommendations.
You can review and disable this under Web & App Activity in your Google Account Security Checklist.
4. App Permissions Abuse
Some apps request unnecessary access to camera, contacts, storage, or location — even when not required for their core function.
To audit risky apps, follow this detailed guide on checking and fixing dangerous app permissions on Android. You should also monitor recent permission usage through the Android Privacy Dashboard.
Key takeaway: Tracking happens through permissions and activity data. Regularly reviewing these settings keeps you in control of your digital privacy.
Ad Personalization & Data Profiling
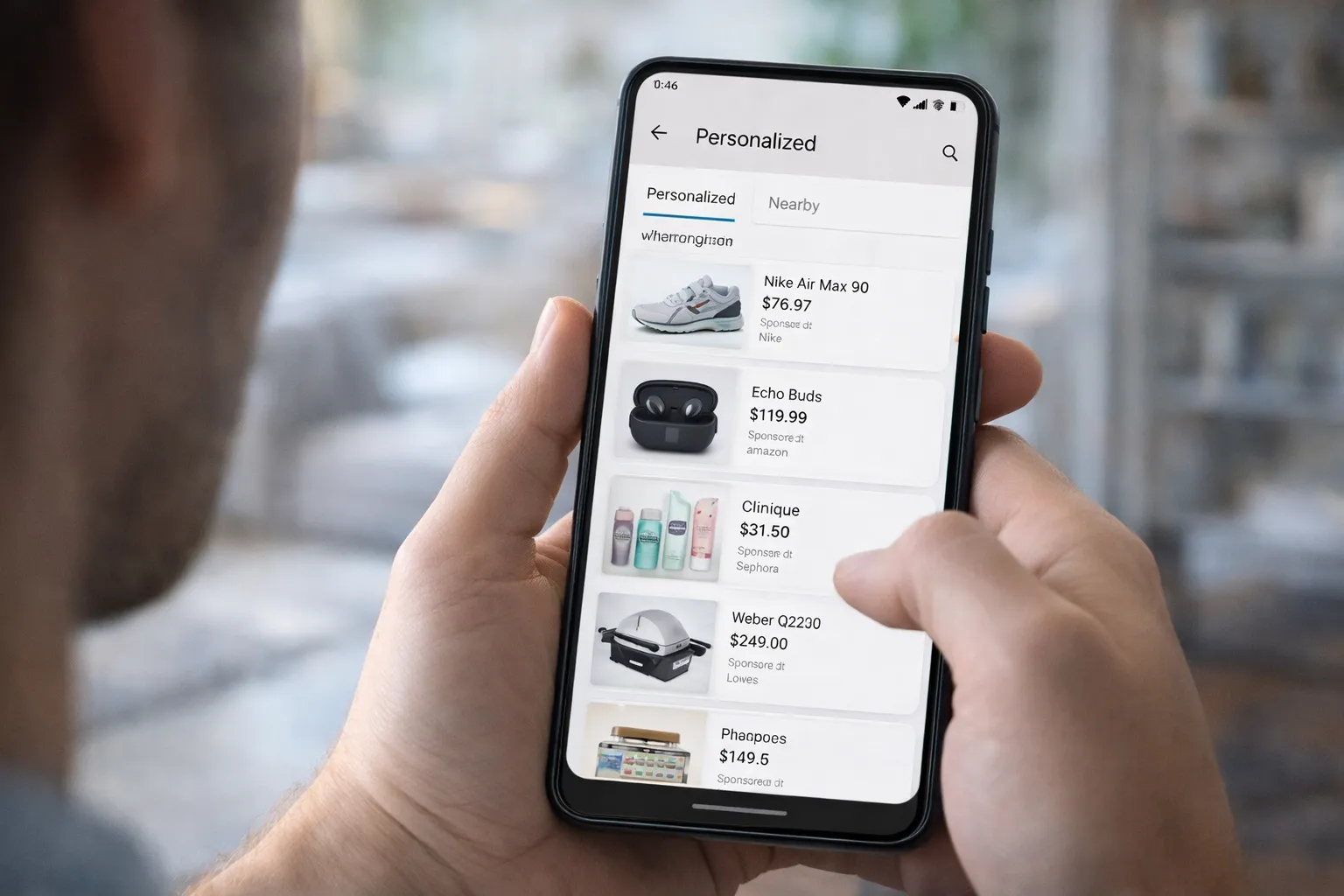
Ad personalization is one of the main reasons people feel their phone is “listening.” In reality, it works through data profiling — not secret audio recording.
Here’s how ad personalization typically works in 2026:
- Search Activity: Queries on Google and YouTube shape your interest profile.
- Website Visits: Browsing shopping, finance, or tech sites adds behavioral signals.
- App Engagement: The apps you use frequently help categorize your interests.
- Location Patterns: Regular visits to certain places influence lifestyle-based ads.
- Ad Interaction History: Ads you click, skip, or watch improve targeting accuracy.
All of this data is combined to create a digital profile that predicts what you might be interested in next. That’s why ads often feel surprisingly accurate.
If you want to reduce this profiling, you can:
- Turn off Ad Personalization in your Google settings
- Disable Web & App Activity
- Clear your advertising ID periodically
For step-by-step instructions, follow our Google Account Security Checklist (2026) and review app-level tracking using the Android Privacy Dashboard.
Important: Ad personalization is automated and algorithm-driven. While it improves relevance, limiting data collection gives you stronger privacy control and reduces behavioral profiling.
Why This Can Be a Privacy Problem
Even if your phone isn’t secretly listening, excessive data tracking can still create serious privacy risks. The issue isn’t constant recording — it’s the amount of behavioral data collected over time.
Here’s why this matters:
- Personal Data Profiling: Companies build detailed interest profiles based on your searches, app usage, and location patterns.
- Targeted Manipulation: Highly personalized ads can influence buying decisions and even opinions.
- Location Exposure Risks: Continuous location tracking can reveal daily routines and sensitive places you visit.
- Data Leaks: If a service suffers a breach, your stored data could be exposed.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Apps with excessive permissions increase the attack surface for malware.
Many privacy risks happen quietly in the background. That’s why reviewing permissions and activity settings regularly is essential.
If you suspect unusual behavior — such as unknown apps, unexpected battery drain, or strange pop-ups — read our detailed guide on how to check if your phone is hacked or spied on.
You should also audit risky permissions using this step-by-step guide on fixing dangerous app permissions.
Bottom line: The real privacy problem isn’t microphone spying — it’s uncontrolled data collection. Limiting tracking and managing permissions reduces both profiling risks and security threats.
Disable Microphone Access on Android
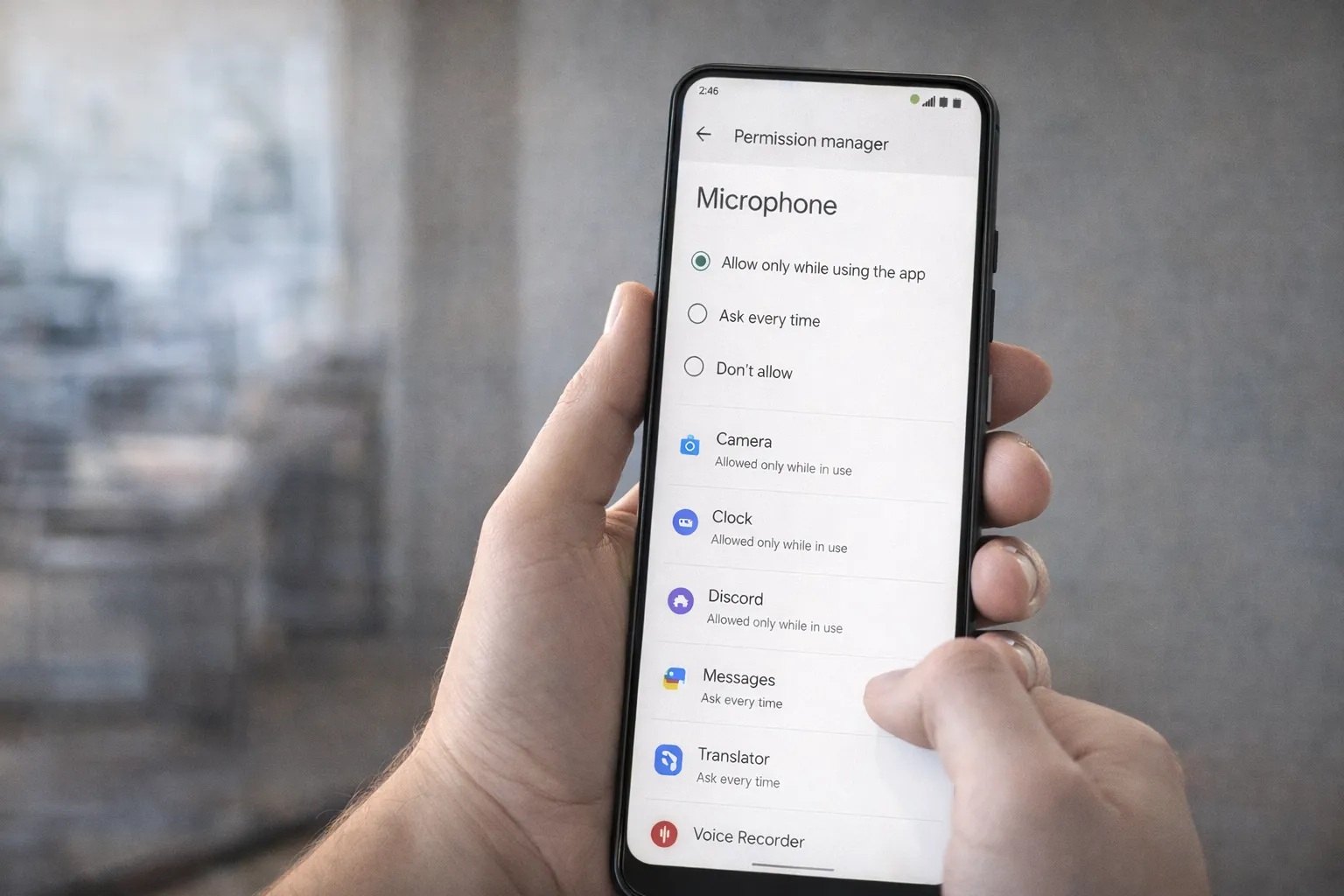
If you're concerned about privacy, one of the first steps is reviewing which apps can access your microphone. While Android does not allow apps to record without permission, limiting access adds an extra layer of security.
Follow these simple steps to disable unnecessary microphone access:
- Open Settings on your Android phone.
- Tap Privacy.
- Select Permission Manager.
- Tap on Microphone.
- Review the list of apps and remove access from any app that doesn’t truly need it.
For better control, choose one of these options where available:
- Allow only while using the app
- Ask every time
- Don’t allow
Pro Tip: Avoid granting microphone access to flashlight, wallpaper, or utility apps — they typically don’t need it.
Regularly auditing permissions ensures that your device stays secure and that no app has unnecessary access to sensitive hardware features.
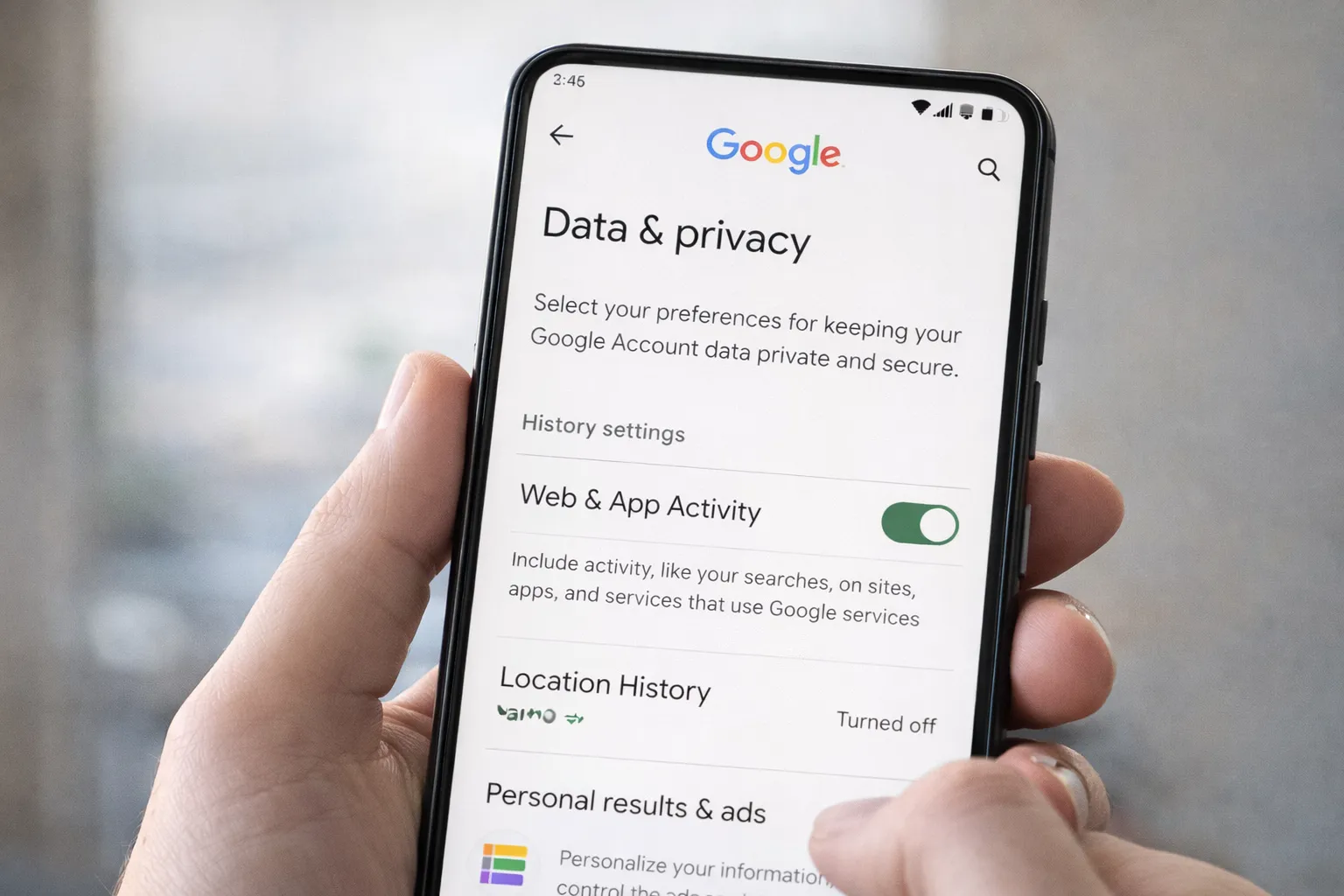
Turn Off Google Ad Personalization
If you want to reduce targeted ads and limit behavioral profiling, turning off Google Ad Personalization is an important step. While this won’t stop ads completely, it will prevent Google from using your activity data to customize them.
Here’s how to turn it off on Android (2026 method):
- Open Settings on your phone.
- Scroll and tap Google.
- Select Manage your Google Account.
- Go to the Data & Privacy tab.
- Find Ad Settings or My Ad Center.
- Turn off Personalized Ads.
You should also review these related settings:
- Web & App Activity – Tracks searches and app interactions
- Location History – Stores places you’ve visited
- YouTube History – Influences video recommendations and ads
For a full security checklist, follow our detailed guide: Google Account Security Checklist (2026).
Even after disabling ad personalization, Google may still show ads — but they’ll be less tailored to your behavior.
Important: Turning this setting off reduces data profiling but does not delete past activity. You may want to manually review and delete stored activity from your Google account for stronger privacy control.
Disable Web & App Activity Tracking
Web & App Activity is one of the main settings that allows Google to store your searches, app usage, and browsing behavior. Disabling it significantly reduces personalized tracking across Android, Chrome, and other Google services.
Here’s how to turn it off in 2026:
- Open Settings on your Android device.
- Tap Google.
- Select Manage your Google Account.
- Go to the Data & Privacy section.
- Find Web & App Activity.
- Toggle it Off and confirm your choice.
You can also enable Auto-delete to automatically remove stored data after 3, 18, or 36 months.
Disabling this setting stops Google from saving:
- Search queries
- Google Assistant interactions
- App activity linked to your account
- Browsing data from Chrome (if synced)
Pro Tip: Turning off Web & App Activity may slightly reduce personalized recommendations, but it greatly improves privacy control and limits behavioral data storage.
Use Android Privacy Dashboard to Monitor Apps
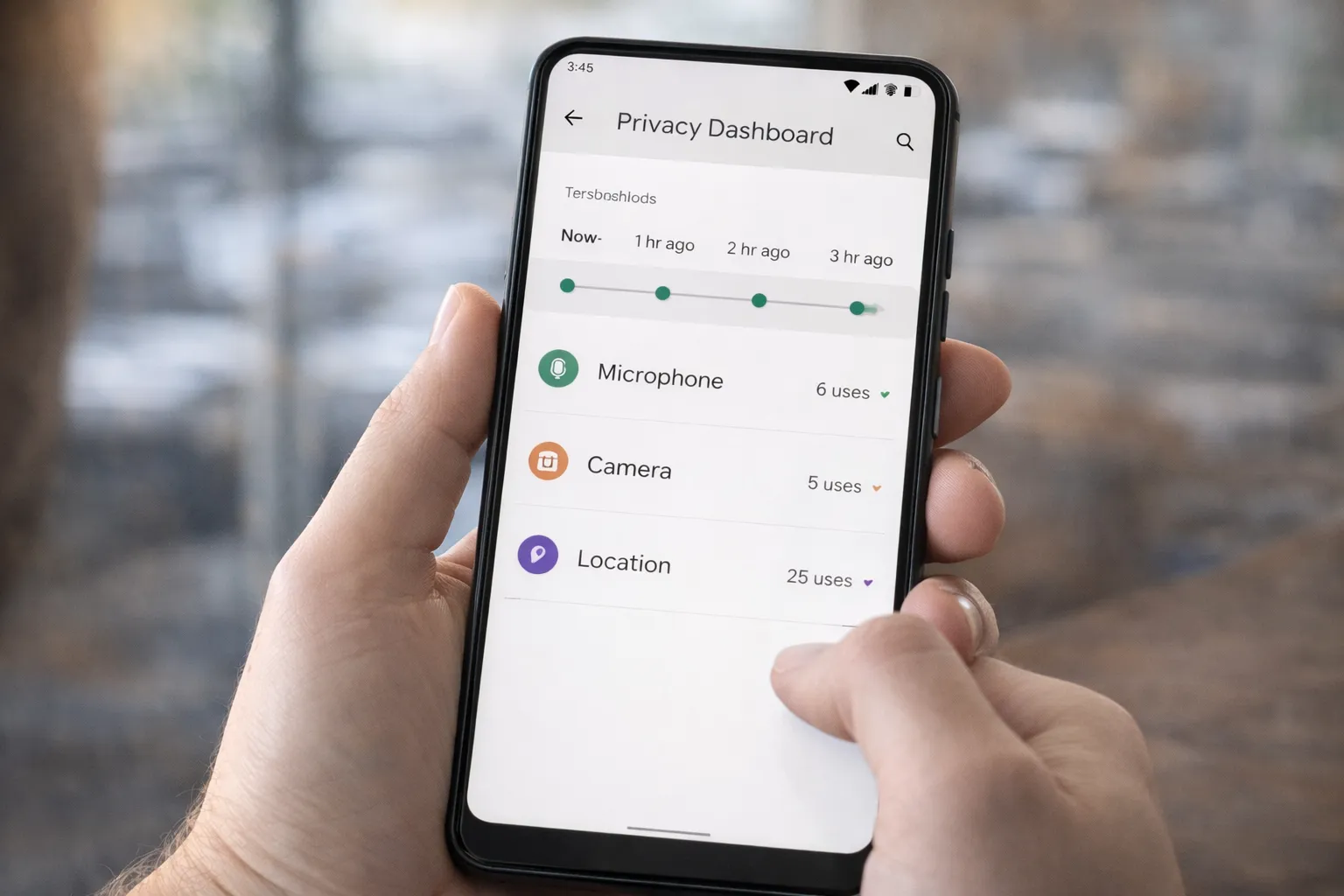
If you want real visibility into what your apps are accessing, the Android Privacy Dashboard is one of the most powerful built-in tools available in 2026. It shows exactly which apps accessed sensitive permissions like camera, microphone, and location.
Here’s how to access it:
- Open Settings on your Android phone.
- Tap Privacy.
- Select Privacy Dashboard.
Inside the dashboard, you can view:
- Microphone access history (last 24 hours)
- Camera usage by apps
- Location access timeline
- Permission usage breakdown
This allows you to quickly identify apps that are accessing permissions unexpectedly. If you notice suspicious activity, you can immediately revoke access from the same screen.
For a deeper understanding, read our full guide on how the Android Privacy Dashboard works.
You should also combine this with regular permission audits using our guide on checking and fixing dangerous app permissions.
Best practice: Review your Privacy Dashboard at least once a month. Monitoring permission access proactively is one of the most effective ways to prevent unwanted tracking and improve overall device security.
Step-by-Step: How to Stop Tracking on Android (2026)
If you want stronger privacy on your Android device, follow these practical steps. Together, they significantly reduce tracking, profiling, and unnecessary data collection.
Step 1: Turn Off Microphone Access
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Privacy.
- Select Permission Manager.
- Open Microphone.
- Remove access from apps that don’t genuinely need it.
This ensures no unnecessary app can access your audio input.
Step 2: Disable Google Ad Personalization
- Open Settings.
- Tap Google.
- Select Manage your Google Account.
- Go to Data & Privacy → Ad Settings.
- Turn off Personalized Ads.
Step 3: Turn Off Web & App Activity
- Open your Google Account.
- Tap Data & Privacy.
- Disable Web & App Activity.
For complete account protection, follow our how to check if your phone is hacked or spied on
Step 4: Disable Background Location
- Go to Settings → Location.
- Open App Location Permissions.
- Select Allow only while using the app where possible.
Step 5: Use Privacy Dashboard
The Privacy Dashboard shows recent access to camera, microphone, and location. Review it regularly to detect suspicious activity.
Learn how it works in detail here: Android Privacy Dashboard Explained.
Result: These five steps together reduce behavioral tracking, limit profiling, and give you stronger control over your Android privacy in 2026.
Final Verdict
Your phone is not secretly recording your conversations for advertising. The idea sounds alarming, but there is no solid evidence that smartphones constantly spy through the microphone.
However, data tracking is very real. Companies use permissions, browsing activity, location history, and AI-based profiling to understand user behavior. That’s why ads can feel extremely accurate — even without audio recording.
The good news? You are in control.
By adjusting a few key settings, you can significantly reduce tracking on Android in 2026:
- Review and limit microphone, camera, and location permissions
- Disable Web & App Activity in your Google account
- Turn off Ad Personalization
- Regularly check the Privacy Dashboard
- Remove risky or unnecessary apps
Bottom line: Your phone isn’t secretly listening — but smart algorithms are constantly analyzing digital signals. The more you manage permissions and activity settings, the stronger your privacy will be.
Digital awareness is the best defense. Stay informed, stay updated, and take control of your Android privacy today.